Time management is one of the most critical skills for a project manager, where juggling multiple tasks, deadlines, and team responsibilities is the norm. This guide will explore key methods like time blocking, prioritization, and other actionable techniques that can help you streamline your workday and boost productivity without adding hours to your schedule.
Key Concepts for Getting More Done with Less Time
1. Time Blocking

What It Is: Time blocking involves scheduling dedicated chunks of time for specific tasks or categories of work. Instead of multitasking, you focus intensely on one task during a set period.
Pros:
- Reduces context switching, leading to more focus.
- Helps prevent burnout by scheduling breaks and work boundaries.
- Gives a clear overview of how your day will unfold.
Cons:
- Requires discipline and sticking to the schedule.
- Unexpected events may force you to rearrange blocks
How to Implement: Use a digital calendar or a planner to block out chunks of time for key project activities—e.g., team meetings, deep work sessions, and communication with stakeholders.
2. Prioritization (Eisenhower Matrix)
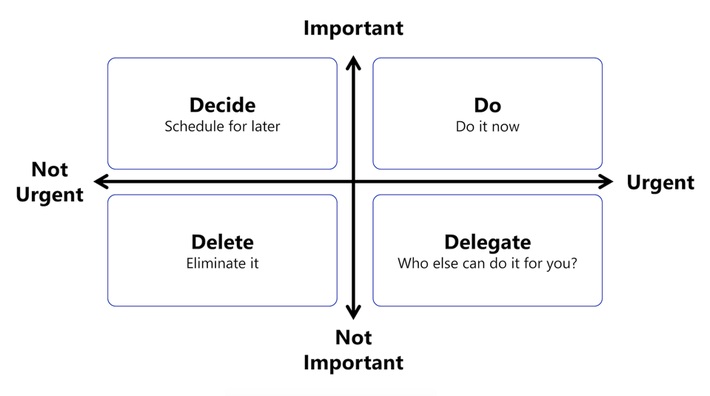
What It Is: Prioritization frameworks like the Eisenhower Matrix allow you to categorize tasks into four quadrants based on urgency and importance:
- Urgent and Important (Do first)
- Important, Not Urgent (Schedule)
- Urgent, Not Important (Delegate)
- Not Urgent, Not Important (Eliminate)
Pros:
- Ensures you focus on high-impact tasks.
- Helps you delegate less important tasks.
- Encourages eliminating unnecessary work.
Cons:
- Takes time to categorize tasks correctly.
- May overlook tasks that could evolve into high-priority issues.
How to Implement: Review your to-do list daily and categorize each task based on urgency and importance. Focus on high-priority tasks early in the day.
3. Pomodoro Technique
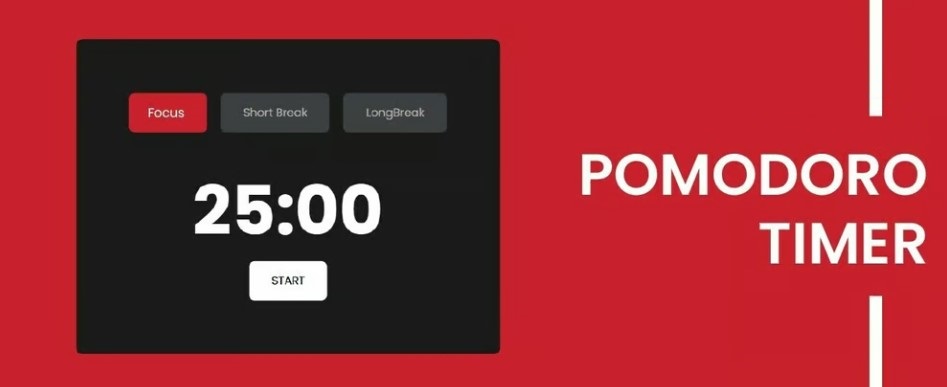
What It Is: A time-management method where you work in 25-minute intervals (Pomodoros) with 5-minute breaks in between. After four sessions, take a longer break.
Pros:
- Encourages focused work while preventing burnout.
- Forces regular short breaks to refresh your mind.
- Can make overwhelming tasks seem more manageable.
Cons:
- Not ideal for tasks requiring deep, prolonged concentration.
- Interruptions can break the flow, making it hard to resume the Pomodoro session.
How to Implement: Use a timer to break work into Pomodoros. Adjust the work intervals if necessary (e.g., 25 minutes of work followed by a 5-minute break).
4. The Two-Minute Rule

What It Is: If a task takes less than two minutes, do it immediately. This method is part of the Getting Things Done (GTD) system and helps prevent small tasks from accumulating.
Pros:
- Quickly clears low-effort tasks off your list.
- Keeps your task list leaner and more focused.
Cons:
- Overusing this method can distract from larger, more important tasks.
- Not suitable for complex tasks or deep work sessions.
How to Implement: Regularly review your task list and immediately handle any tasks that take less than two minutes. For larger tasks, schedule time to complete them.
5. Batching Tasks
What It Is: Batching involves grouping similar tasks (like replying to emails, updating project statuses, or doing administrative work) into one block of time, reducing task-switching fatigue.
Pros:
- Increases efficiency by handling repetitive tasks together.
- Minimizes distractions from switching between different types of work.
Cons:
- Some tasks may not fit neatly into a batch.
- Requires careful scheduling to avoid task pile-ups.
How to Implement: Identify recurring tasks that can be batched and schedule them into specific time blocks (e.g., answering emails twice a day instead of checking constantly).
Pros and Cons of These Methods:
Pros:
- Greater productivity and focus by minimizing multitasking.
- More structured workdays with dedicated time for priority tasks.
- Less mental fatigue by grouping similar tasks or using time-based intervals like Pomodoros.
Cons:
- These methods require discipline and consistency to maintain.
- Unexpected events can disrupt carefully planned schedules.
- Some methods, like time blocking or task batching, can feel restrictive if not implemented flexibly.
Implementation Plan:
Step 1: Choose Your Core Method
Start by picking one method that resonates with your work style. For example, if you struggle with multitasking, begin with time blocking. If decision-making is the challenge, start with prioritization using the Eisenhower Matrix.
Step 2: Set Up Your Tools
Utilize digital calendars, task management apps, or even simple spreadsheets to organize your time and tasks. Tools like Asana, Trello, or Google Calendar can make time blocking, task batching, and prioritization easier to manage.
Step 3: Begin Small, Then Scale
Start by implementing your chosen technique for just one or two days a week. Once you get comfortable, scale it to more days and integrate additional methods like Pomodoros or task batching.
Step 4: Review and Adjust
At the end of each week, review your time management strategy. What worked? What didn’t? Adjust your approach to suit your work style, priorities, and project demands.
Scaling Time Management for Maximum Efficiency
Mastering time management takes practice, but the rewards are clear. By implementing a mix of strategies like time blocking, prioritization, and batching, you can significantly enhance your productivity while maintaining a healthy work-life balance. Start small, be consistent, and scale your approach as your comfort grows — soon, you’ll find that you’re getting more done in less time, with less stress.